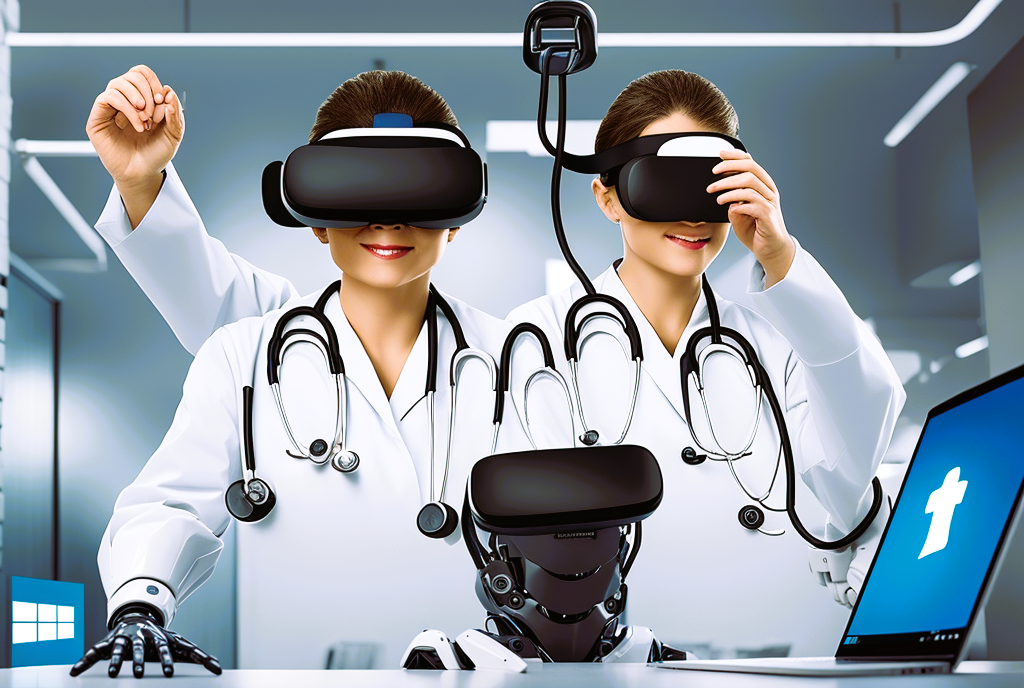
In the realm of physical therapy, technological innovations continue to revolutionize the way clinicians approach rehabilitation and patient care. Among these advancements, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) have emerged as powerful tools with the potential to transform traditional physical therapy interventions. By immersing patients in interactive virtual environments or overlaying digital information onto the real world, VR and AR offer new possibilities for enhancing motor learning, functional recovery, and patient engagement. This article explores the applications of VR and AR in physical therapy and their impact on rehabilitation outcomes.
Understanding Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality
Virtual reality refers to computer-generated simulations that immerse users in realistic, interactive environments, typically through the use of head-mounted displays (HMDs) and motion tracking technology. In contrast, augmented reality overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of their surroundings through devices such as smartphones, tablets, or smart glasses.
Both VR and AR technologies offer unique advantages for physical therapy interventions:
- Immersive Experiences: VR allows patients to engage in virtual environments that simulate real-world activities and scenarios, providing a high degree of immersion and presence. AR supplements the real world with digital information, enabling patients to interact with virtual objects overlaid onto their physical surroundings.
- Interactive Feedback: VR and AR systems can provide real-time feedback on patient performance, allowing therapists to monitor movement patterns, technique, and progress during rehabilitation exercises. This immediate feedback enhances motor learning and enables therapists to adjust interventions in real time.
- Customization and Personalization: VR and AR applications can be tailored to meet the individual needs, preferences, and abilities of patients, allowing for personalized rehabilitation programs. Therapists can adjust the difficulty level, pace, and content of virtual exercises to match each patient’s goals and functional status.
Applications of VR and AR in Physical Therapy
The integration of VR and AR into physical therapy practice has led to a wide range of innovative applications across various clinical settings:
- Pain Management: VR has been shown to be effective in reducing pain perception and improving pain management outcomes for patients with chronic pain conditions. By distracting patients from their pain through immersive virtual experiences, VR can help alleviate discomfort and promote relaxation during therapy sessions.
- Neurorehabilitation: VR-based rehabilitation programs have been developed to facilitate motor recovery and functional independence in patients with neurological conditions such as stroke, traumatic brain injury, and spinal cord injury. These programs use interactive virtual environments to promote upper limb, lower limb, and balance training through task-specific exercises and gaming activities.
- Gait Training: VR and AR systems can be used to enhance gait training interventions for individuals with gait impairments or mobility limitations. By providing visual and auditory cues, feedback on gait parameters, and virtual environments with varying terrain and obstacles, these technologies can improve gait symmetry, stability, and endurance.
- Balance Rehabilitation: VR-based balance training programs challenge patients to maintain postural stability and control while interacting with virtual environments that simulate dynamic or unstable surfaces. These exercises help improve balance, proprioception, and vestibular function in patients with balance disorders or fall risk. Did you like the article? Read also about Innovations in hydrotherapy.
- Patient Education and Home Exercise Programs: VR and AR applications can be used to educate patients about their conditions, treatment options, and rehabilitation exercises. Therapists can create immersive educational experiences that empower patients to take an active role in their recovery and adhere to home exercise programs.
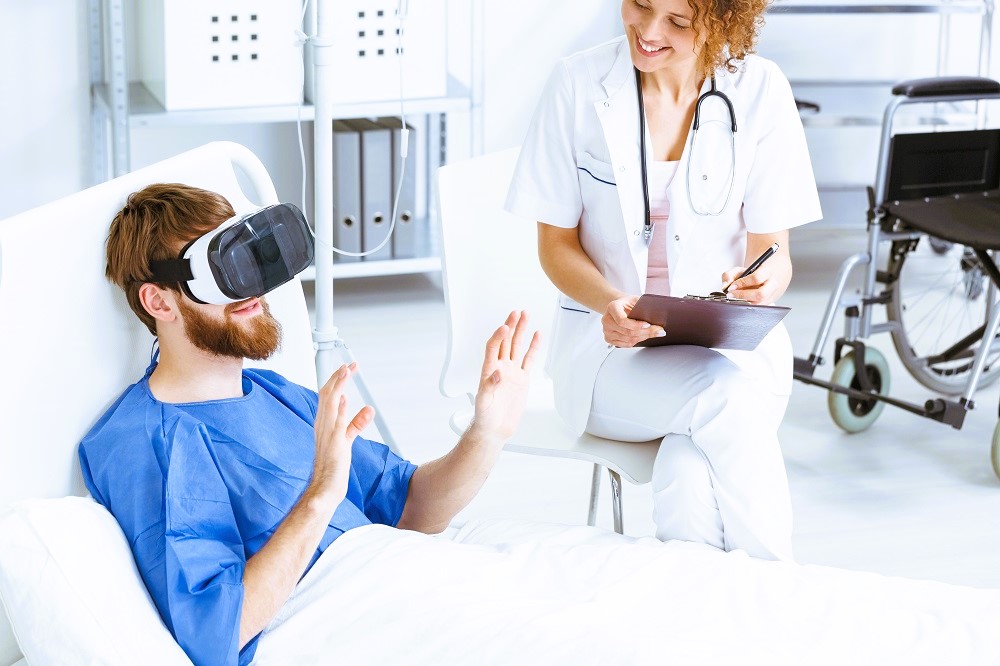

Challenges and Considerations
While the potential benefits of VR and AR in physical therapy are significant, several challenges and considerations must be addressed to maximize their effectiveness and adoption:
- Equipment and Cost: VR and AR systems require specialized hardware, software, and technical expertise, which may pose barriers to adoption for some clinics or patients. Cost-effective solutions and reimbursement models are needed to ensure equitable access to these technologies.
- Usability and User Experience: The user interface, interaction design, and comfort of VR and AR systems play a crucial role in patient engagement and adherence to therapy. User-friendly interfaces, intuitive controls, and comfortable HMDs are essential for creating positive experiences and minimizing discomfort.
- Evidence-Based Practice: While there is growing evidence supporting the efficacy of VR and AR in physical therapy, further research is needed to establish standardized protocols, best practices, and clinical guidelines for their use. Rigorous studies are required to evaluate the long-term effects, cost-effectiveness, and comparative effectiveness of VR and AR interventions across different patient populations and settings.
Conclusion
Virtual reality and augmented reality have the potential to revolutionize physical therapy interventions by providing immersive, interactive, and personalized experiences that enhance motor learning, functional recovery, and patient engagement. From pain management and neurorehabilitation to gait training and balance rehabilitation, the applications of VR and AR in physical therapy are diverse and promising.
For further information on the standardization of VR and AR technologies in healthcare, visit Wikipedia’s page on Virtual reality in healthcare.
As VR and AR technologies continue to evolve and become more accessible, their integration into physical therapy practice holds tremendous potential for improving outcomes, expanding treatment options, and transforming the delivery of care for patients with musculoskeletal, neurological, and functional impairments. By embracing these innovative technologies and leveraging their capabilities, physical therapists can unlock new opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and transformative rehabilitation experiences.